Inventory best practices
There are a number of things you can do when you set up items that will make it significantly easier for you to manage things like discounts, ordering from suppliers, printing labels, and generating informative reports.
Use the UPC or EAN code for the item lookup code
Universal Product Code (UPC) is a product identification system that is typically used in the U.S. to identify items at the point of sale. In this system, every item sold has its own unique UPC code. For example, a case of bottled water has its own UPC code, but if you break out the bottles of water to sell individually the bottles have a different UPC code from the case.
European Article Number (EAN) is a product identification system that is compatible with UPC that is typically used in Europe to identify items at the point of sale. In many cases the UPC and EAN codes are the same.
Using the UPC or EAN code for the item lookup code has a number of advantages:
-
Consistency: Your item lookup code naming will always be consistent. This makes it easier to look up items, and it results in more professional-looking receipts, work orders, and purchase orders.
-
Specificity: Each UPC or EAN code is unique to a single item and cannot be confused with another item at the point of sale.
-
Universality: UPC and EAN codes are used worldwide by manufacturers, suppliers, and other merchants.
-
Labeling: UPC and EAN codes also make product labeling easier. Almost every product sold has a UPC or EAN printed on it by the manufacturer. This means you can put a price label on the shelf instead of adding a price label to each item individually.
-
Reporting: UPC and EAN codes can also make reporting easier. For example, most UPC codes are 12 digits. The first 6 digits are assigned to the manufacturer, including a check digit, and the next 6 digits identify the product, including a check digit. When generating reports you can use the Filter to include all products that have the same first 6 digits (that is, they have the same manufacturer).
Be consistent when you write item descriptions
If you are setting up your store database for the first time - or are cleaning up and optimizing an existing store database - you should aim for consistency in how you write item descriptions. This makes it easier to search for items, but it also results in more professional-looking receipts, work orders, and purchase orders.
Consider setting up store rules for how you write item descriptions. For example:
-
Capitalization: As a general rule, always follow the capitalization used for trademarked company and product names, for example iPhone. But how should you capitalize other words in the description like "adapter" or "charging cable" or "case" or "earbuds"? For consistency, use either title case or lower case, but not a mix of both. For example:
-
Title case: iPhone Silicone Case
-
Lower case: iPhone silicone case
-
Content: The description field is limited to 30 characters or less, so your item descriptions should be concise and limited to the most important information. To save space, you might decide to not include the manufacturer name in the item description. You can put the manufacturer name in a custom field to aid with searching and filtering. Instead, use the description field just for the product name, for example AirPods Pro earbuds.
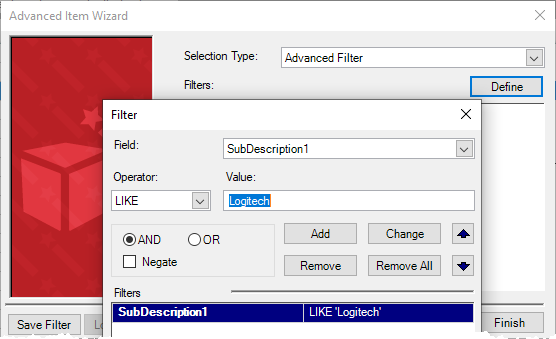
Use custom fields to aid with filtering
You can use filters with a number of different tools in Store Manager, such as:
-
Advanced Item Wizard
-
Purchase Order Requisitions
-
Reports
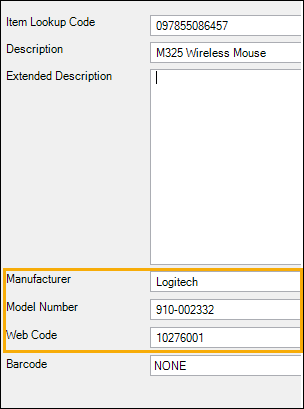
Consider using the customizable item fields (Sub Description 1, Sub Description 2, Sub Description 3) to aid with filtering. For example, you might use the customizable fields to enter the manufacturer, model number, or other stock keeping information such as SKU or web code.

|
|
Note: You customize these field labels in Setup | Miscellaneous | Custom Fields on the Item tab.
This is extremely useful if you want to use the filter to include all items from a particular manufacturer, for example to put those items on sale or to pull sales or to generate reports: